5 Ways Gastroscopy Helps in Detecting Celiac Disease
Last update : 31 Oct 2025
Gastroscopy is an effective diagnostic tool for detecting stomach-related diseases. Also known as Upper GI endoscopy, doctors prefer this to diagnose celiac disease.
Celiac disease refers to an autoimmune condition where your immune system reacts to gluten. This often results in damaging the small intestine. Eating gluten while having this disease accounts for triggering an immune response to this protein in the small intestine. Hence, the lining of the small intestine is affected, and it fails to perform nutrient absorption.
In Canada, celiac disease is present in 1% of the population. Gastroscopy is considered to diagnose this disease, as it executes a microscopic evaluation of the lining of the small intestine. Therefore, it becomes easy to understand how it has been damaged by gluten. This article points out 5 ways in which celiac disease is detected by the gastroscopy procedure.
Gastroscopy and Its Working Process
Gastroscopy refers to a test that examines the interior of your upper digestive system (throat, oesophagus, and stomach). Based on this test, a patient understands the reason behind the existing symptoms.
Referring to the procedure, a thin and flexible tube is inserted from the mouth to the throat to the stomach. This tube contains a camera, which captures the inside of the upper digestive system. This diagnosis procedure has a wide acceptance because it accounts for a direct visual inspection while diagnosing a disease in real-time.
The gastroscopy procedure is completed within 15 to 45 minutes. Let’s check out what happens and how you might feel.
| What Happens | How You Feel |
| Insertion of a thin pipe into the stomach | A feeling of sickness occurs, but it stops once the tube reaches the stomach. Often, doctors give sedatives. |
| Pumping of air for inflating the stomach | Feel of bloating and burping several times |
| Obtaining a tissue sample (Not always) | No feelings |
Table 1: Different Aspects During Gastroscopy
Top Complications of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease can account for a range of complications if you ignore proper treatment.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition happens when the small intestine fails to absorb adequate nutrients. This can result in weight loss and anaemia.
- Bone weakening: Ignoring celiac disease can lead to softening of the bone or loss of bone density. This results in osteomalacia in children and osteoporosis in adults.
- Miscarriage: Celiac disease, if left untreated, can make women unable to absorb Vitamin D and calcium. This can result in miscarriage.
Choosing a perfect diagnosis method is important so that celiac disease is treated perfectly. Therefore, the gastroscopy procedure is a suitable choice.
What Are the 5 Ways in Which Celiac Disease is Detected by Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy is a common consideration when it comes to testing for celiac disease. Here are the major ways in which celiac disease is detected by this procedure.
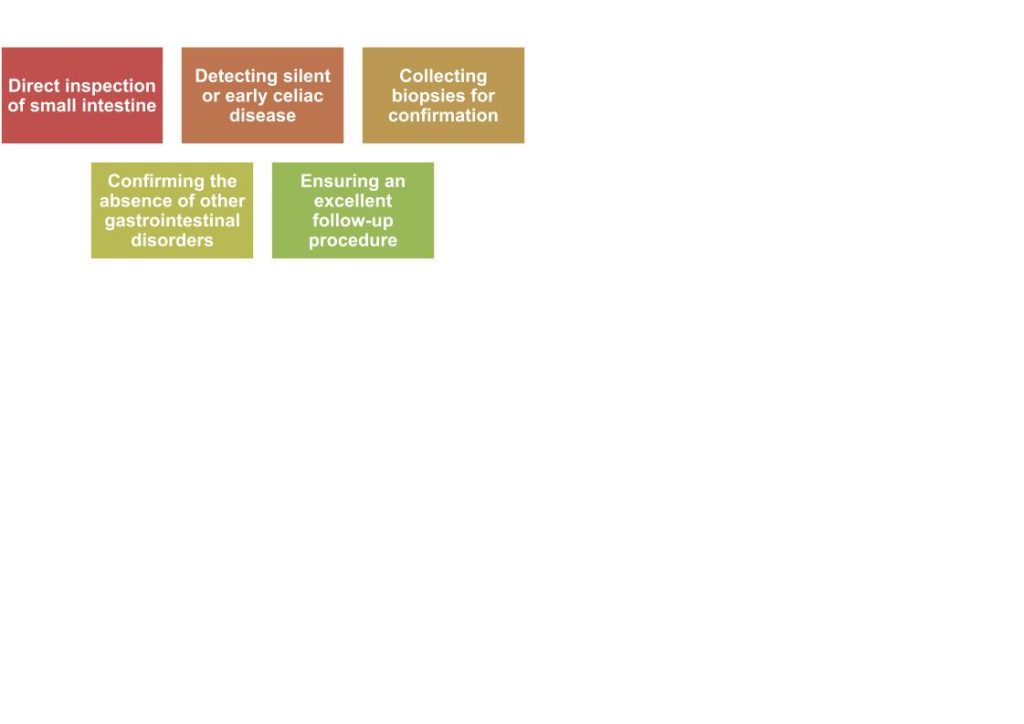
Figure: 5 Ways to Detect Celiac Disease by Gastroscopy
1. Direct Inspection of the Small Intestine
Gastroscopy offers a comprehensive view of your small intestine, which is an essential condition for detecting celiac disease. Doctors visualise the lining of the organ to identify different signs of villous atrophy, like fissures, folds, etc.
If you have celiac disease, there might be some sort of inflammation in the stomach lining. A blood test cannot detect it, but the gastroscopy procedure can. This confirms the presence of the disease so that the doctor can go for another treatment procedure. Here is a comparison between a blood test and a gastroscopy.
| Aspects | Blood test | Gastroscopy |
| Method | Simply a drawing of blood | An invasive process to inspect the digestive tract |
Scope | A general test | Applicable specifically to the upper digestive system |
| Outcome | Offering indirect evidence of issues | Providing accurate results because of direct visualisation |
Table 2: Blood Test vs Gastroscopy
This shows that a gastroscopy is better than a blood test for detecting celiac disease. Therefore, this diano procedure is preferred by the doctors.
2. Detecting Silent or Early Celiac Disease
Testing for celiac disease is difficult in several cases because no symptoms are experienced by the patients. This accounts for silent celiac disease. Here, gluten damages the small intestine but the concerned individual does not get any symptoms.
The main symptoms of celiac disease are bloating, constipation, diarrhoea, etc. Well, a person might not experience any symptoms in the initial stage. Gastroscopy is capable of detecting celiac disease even in the early stage. This benefits a patient because treatment gets started before any severe damage.
3. Collecting Biopsies for Confirmation
Biopsy collection is significant for celiac disease because a definitive confirmation of intestinal damage is obtained. This shows the vitality of gastroscopy in this disease.
The doctor undertakes a full examination of the duodenum, thereby taking 4-6 tissue samples from multiple areas. This is followed by the analysis of the biopsies by a pathologist. Hence, the presence of villous damage is confirmed. This also helps to know if there is any increase in lymphocytes.
4. Confirming the Absence of Other Gastrointestinal Disorders
The symptoms of celiac disease might be the same as several gastrointestinal diseases, like IBS, IBD, NCGS, etc. Not every diagnostic procedure can distinguish one gastrointestinal disease from another. Here, the gastroscopy procedure is highly effective.
The symptoms of the stated diseases might not differ, but they pose different impacts on the health condition in the long term. This indicates the need for a definitive diagnosis. Therefore, gastroscopy is the best option to detect celiac disease.
5. Ensuring an Excellent Follow-Up Procedure
A patient needs to follow specific considerations while healing from celiac disease. In this respect, the contribution of gastroscopy is also important. Doctors execute a perfect monitoring of the treatment response. This ensures mucosal healing.
Doctors advise a gluten-free diet for patients to ensure better recovery from celiac disease. Hence, your stomach lining starts improving.
How to Prepare for Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy is effective in diagnosing celiac disease. Well, a patient must consider several preparations before appearing for this procedure. You must not consume anything for at least 6-8 hours before the test. Water is allowed up to a couple of hours before the procedure, but consulting with your doctor is important. Remember, an empty stomach gives the best view in gastroscopy. This accounts for an accurate diagnosis of celiac disease.
What are the Main Side Effects of Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy has a wide consideration in testing for celiac disease. However, patients must be aware of the common side effects. These include:
- Bloating
- Sore throat
- Drowsiness (due to sedation)
- Bleeding during the biopsy (rare)
Final Thoughts
Celiac disease can lead to complications such as anaemia and osteomalacia, if proper treatment is not acknowledged. Gastroscopy is suitable for treating this disease as it carries out an extensive evaluation of the upper digestive system. This is also effective in detecting silent celiac disease. Patients can feel bloated during the procedure.
Getting the Perfect Treatment for Celiac Disease
Celiac disease must not be ignored. Over other diagnostic processes, gastroscopy has shown wider acceptance. Hence, the disease is detected accurately. Our highly skilled and experienced team can help you in choosing the right path to deal with this disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Celiac Disease an Allergy?
No, celiac disease is not an allergy. This is an autoimmune disorder.
2. Can I Consume Gluten if I Have Silent Celiac Disease?
No, you should not. Preferring gluten in your diet results in intestinal damage even if you are devoid of symptoms.
3. Should I Inform the Doctor About the Medications That I Take Before Gastroscopy?
Yes. Inform your doctor about all the medicines that you take. This includes diabetes medication, blood thinners, etc.
4. What Should Be My Diet Plan After Gastroscopy?
You must eat a soft and light diet for the next two days. Avoid spicy foods and alcohol.
